-
Developing Diagnostic Assessments to Improve Data-Driven Instruction
-
Linguistic, Prior Knowledge, Cognition, and Observations involved in assessment creation.
Hearing the words: assessment, evaluation, and data can give you a variety of emotions, ideas, and memories. For a child, assessment is something that can be rudimentary or boring. However, as we know assessments, if delivered accurately can provide insight and knowledge for your child.
Moreover, evaluation tools with the appropriate metrics and information can help you make better-informed decisions. Your evaluations include seeing how a child learns from observations, and formal measures outlined by your district or standards.
Below are a few things to remember when designing assessments or even using a company’s assessment to improve instruction.
Linguistic
Linguistics is a child’s language experience. Their language comes from home experiences as well as the school where the word structure that is picked up in both environments may differ. In Assessing Readers the author poses the questions on what experiences do their families have when it comes to language. Do they sing at home? Are there different native languages?
Prior Knowledge
A child’s existing knowledge or prior knowledge varies. We all come from different experiences and different backgrounds. A learner’s personal experience can determine how they make decisions and even react to certain topics.
For example, if a teacher asked an open-ended question saying, what is a pet. Neither list is wrong but shows that their schema, or body of knowledge, differs because of their experiences and prior knowledge.
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE EXAMPLE
John
-Dog
-Cat
Ericka
-Guinea pig
-Lizard
Cognition
Our cognition can be categorized as schema. “Fulbrook shares schema here
“Schemas are categories of information stored in long-term memory. A schema contains groups of linked memories, concepts, or words. This grouping of things acts as a cognitive shortcut, making storing new things in your long-term memory and retrieval of them much quicker and more efficient.-Fulbrook
- Schemata have variables
- Schemata can embed one with another
- Schemata represents generic to abstract concepts
- Schemata represents knowledge from experiences rather than definitions.
Schema is an educational and brain theory that explains how knowledge is constructed and organized in someone’s mind.
Affective
Thinking about affective is being empathetic about the child’s emotions/attitudes, interests, feelings, and needs. If designing an assessment to understand the learner, a basic interest inventory is always useful.
- What do you like about (topic)?
- What do you dislike about (topic)?
- Do you read for fun?
- What is your favorite thing to do, tell me why?
- How do you feel when?
Hopefully from these conversations, you can gather a deeper picture of the learner than before.
Cultural and Sociocultural Influences
While experiences make a difference in a child’s learning, they are at home culture cannot be forgotten. “each is also strongly influenced by an individuals’ cultural and sociocultural background.
When you think about a home where a child speaks Black Language (use examples from Professor) they are accustomed to a language that differs from their academic English skills.
Also, if a child is Deaf or Hard of Hearing and learns American Sign Language. They have to learn the English language syntax, and their deaf culture influences their classroom experience.
“Teachers need to plan assessment and instruction to fairly evaluate a child in their classrooms so that each child is given maximum opportunities and encouragement to succeed.” -Flippo Assessing Readers

Observations
Observing a child gives authentic viewpoints about how he or she acts, thinks, and speaks. These observations can give you different performance metrics. With observations, it is critical to ask open-ended questions and take
Informal Reading Interventions (IRI)
Involve learners reading word lists, and answering questions about their readings.
When grading, you can make an educated guess where the learner is on the Independent Level-Can read a passage on their own with ease and without any support:
Independent Level-can read without support and can comprehend the reading.
Instruction Level-Can read but might need prompting or support to read.
Frustration Level-Struggles to read where multiple mistakes are made, rereading, skipping, or being unable to read the passage at all.
A Running Records are commercially prepared and can also be prepared by educators or professionals. Running records are historically manually given where an educator or professional evaluates one child at a time.
1. Child and teacher sit across from each other.
2. Child reads a short passage out loud.
3. While the child reads, the teacher marks any miscues, repetitions, and more on their sheet. This sheet has the same passage that the child reads but is formatted for markings.
4. Once complete, the teacher will provide another story that is easier or more difficult and continue the same process.
5. Preferably in one session and child reads 1-3 passages, and the teacher also asks a series of questions.
There are so many different assessments especially with commercial assessments: Survey, diagnostic, standardized, norm-referenced, criterion-referenced, grade-level equivalent, and age-level equivalent.
As always do not forget these assessments that are being created could have errors. Over the years, educators have discovered problems with test questions, limitations in context, validity, authenticity, and even relevance. Historically standardized tests and commercially driven assessments have widened the gap making this now an Opportunity Gap.
More here about Standardized Tests
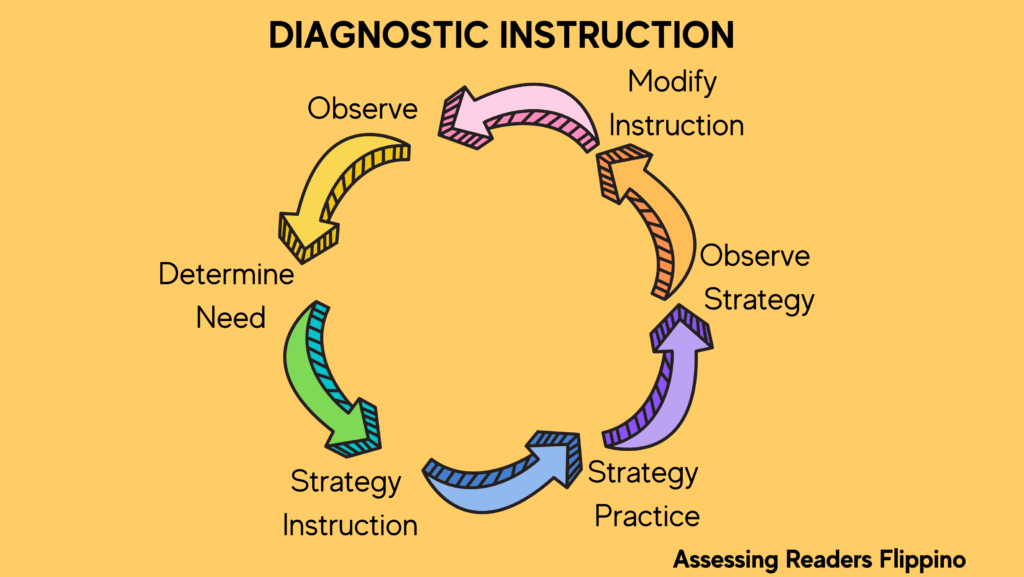
Instruction
With the data gathered from an assessment, you can use the information to create your lesson plans, small group instruction, and units of studies. The assessments should have the insights so you can teach the appropriate skills to move your students forward.
At Pennez, we want to speak with our readers and learn about their educational needs. What is exciting we launched an online tool called Read2Think which delivers running records online using Artificial Intelligence. If you would like to pilot our program, click here.




